pprof
pprof 包含两个,runtime/pprof适用于跑本地程序的场景,net/http/pprof适用于web应用场景
本质上 net/http/pprof是对runtime/pprof的二次封装
runtime/pprof 的使用
package main
import (
"flag"
"log"
"os"
"runtime/pprof"
"sync"
)
func counter() {
slice := make([]int, 0)
c := 1
for i := 0; i < 100000; i++ {
c = i + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5
slice = append(slice, c)
}
}
func workOnce(wg *sync.WaitGroup) {
counter()
wg.Done()
}
func main() {
var cpuProfile = flag.String("cpuprofile", "", "write cpu profile to file")
var memProfile = flag.String("memprofile", "", "write mem profile to file")
flag.Parse()
//采样cpu运行状态
if *cpuProfile != "" {
f, err := os.Create(*cpuProfile)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
pprof.StartCPUProfile(f)
defer pprof.StopCPUProfile()
}
var wg sync.WaitGroup
wg.Add(100)
for i := 0; i < 100; i++ {
go workOnce(&wg)
}
wg.Wait()
//采样memory状态
if *memProfile != "" {
f, err := os.Create(*memProfile)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
pprof.WriteHeapProfile(f)
f.Close()
}
}
通过编译、执行后获得pprof的采样数据,然后就可以利用相关工具进行分析
$ go build main.go
$ ./main --cpuprofile=cpu.pprof
$ ./main --memprofile=mem.pprof
启动pprof 可视化界面
方法一:
$ go tool pprof -http=:8080 cpu.prof
方法二:
$ go tool pprof cpu.prof
$ (pprof) web
另一种查看pprof方式
安装 pprof
$ go get -u github.com/google/pprof
启动 pprof 可视化界面
$ pprof -http=:8080 cpu.prof
如果出现 Could not execute dot; may need to install graphviz. ,就需要安装 graphviz,graphviz官网 下载安装即可
net/http/pprof 的使用
web服务中net/http/pprof以”_” 方式导入,只需要运行该包的init()函数即可,该包自动完成信息采集保存在内存中,所以线上不要使用,影响服务性能
package main
import (
"time"
"net/http"
_ "net/http/pprof"
)
func counter() {
slice := make([]int, 0)
c := 1
for i := 0; i < 100000; i++ {
c = i + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5
slice = append(slice, c)
}
}
func workForever() {
for {
go counter()
time.Sleep(1 * time.Second)
}
}
func httpGet(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
counter()
}
func main() {
go workForever()
http.HandleFunc("/get", httpGet)
http.ListenAndServe("localhost:8000", nil)
}
编译、运行后可通过 http://localhost:8000/debug/pprof/ 查看服务的运行情况,同时不断刷新网页,采样结果也会不断更新
web可视化查看
# 下载 cpu profile,cpu 使用情况,默认从当前开始收集 30s,seconds 参数可指定等待时间
$ go tool pprof http://localhost:8000/debug/pprof/profile?seconds=120
(pprof) web
# 下载 heap profile 采集内存信息
$ go tool pprof http://localhost:8000/debug/pprof/heap
# 下载 goroutine profile
go tool pprof http://localhost:8000/debug/pprof/goroutine
# 下载 block profile
go tool pprof http://localhost:8000/debug/pprof/block
# 下载 mutex profile
go tool pprof http://localhost:8000/debug/pprof/mutex
trace的使用
trace工具也是golang支持的go tool工具之一,能够辅助我们跟踪程序的执行情况,进一步方便我们排查问题,往往配合pprof使用。trace的使用和pprof类似,为了简化分析,我们首先利用下列代码进行讲解,只是用1核运行程序:
本地程序
package main
import (
"os"
"runtime"
"runtime/trace"
"sync"
"flag"
"log"
)
func counter(wg *sync.WaitGroup) {
wg.Done()
slice := []int{0}
c := 1
for i := 0; i < 100000; i++ {
c = i + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5
slice = append(slice, c)
}
}
func main(){
runtime.GOMAXPROCS(1)
var traceProfile = flag.String("traceprofile", "", "write trace profile to file")
flag.Parse()
if *traceProfile != "" {
f, err := os.Create(*traceProfile)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
trace.Start(f)
defer f.Close()
defer trace.Stop()
}
var wg sync.WaitGroup
wg.Add(3)
for i := 0; i < 3; i ++ {
go counter(&wg)
}
wg.Wait()
}
通过编译、执行和如下指令得到trace图
$ go build main.go
$ ./main --traceprofile=trace.pprof
# 通过web查看trace.pprof
$ go tool trace -http=127.0.0.1:8000 trace.pprof
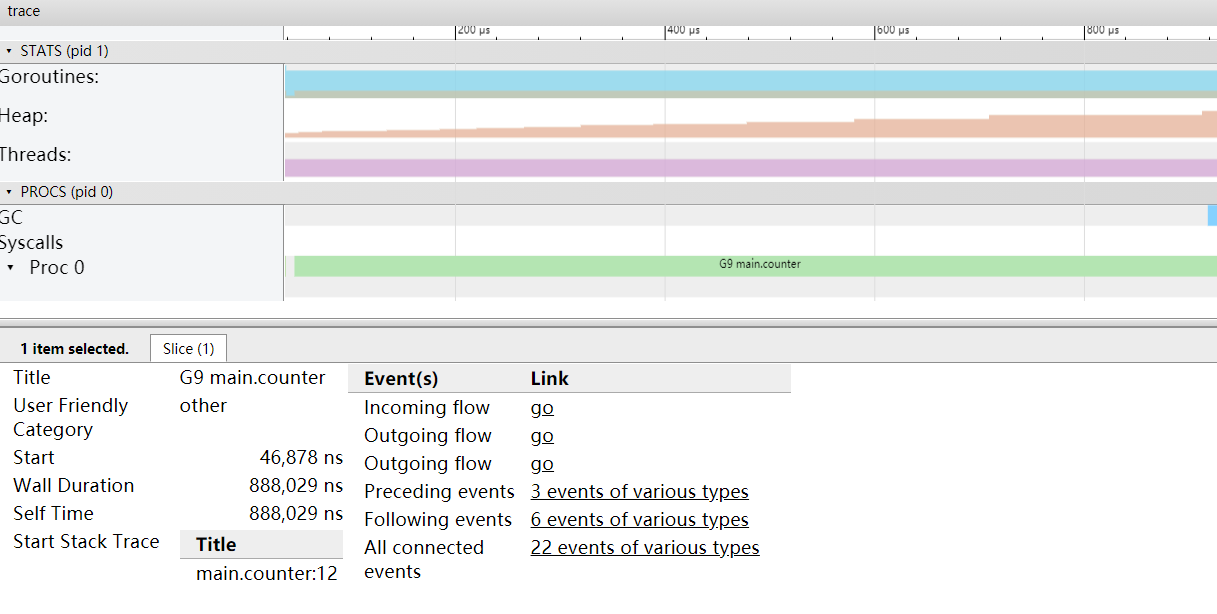
w 放大时间线,s 缩小时间线
web程序
package main
import (
"log"
"net/http"
_ "net/http/pprof"
)
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
s := bigBytes()
if s == nil {
log.Println("oh noes")
}
w.Write([]byte("hello world!"))
})
http.ListenAndServe("127.0.0.1:8080", nil)
}
func bigBytes() *[]byte {
s := make([]byte, 10000000)
return &s
}
web程序不需要引入trace包,否则会再下载trace文件的时候报错,引入pprof包,通过curl 命令下载trace信息
# 使用curl 下载最近5s的 trace 信息
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:8080/debug/pprof/trace?seconds=5 > trace.pprof
# 通过web查看trace.pprof
$ go tool trace -http=127.0.0.1:8000 trace.pprof
参考资料
深度解密Go语言之 pprof
Golang 大杀器之性能剖析 PProf
golang系列—性能评测之pprof+火焰图+trace
