Fasthttp 设计理念
不要分配对象和[]byte缓冲区 - 尽可能多地重用它们
net/http vs Fasthttp
- net/http 的实现是一个连接新建一个 goroutine; fasthttp是利用一个 worker 复用 goroutine,减轻 runtime 调度 goroutine 的压力
- net/http 解析的请求数据很多放在 map[string]string (http.Header) 或 map[string][]string (http.Request.Form),有不必要的 []byte 到 string 的转换,是可以规避的
- net/http 解析 HTTP 请求每次生成新的 http.Request 和 http.ResponseWriter; fasthttp解析 HTTP 数据到 fasthttp.RequestCtx ,然后使用 sync.Pool复用结构实例,减少对象的数量
- fasthttp会延迟解析 HTTP 请求中的数据,尤其是 Body 部分。这样节省了很多不直接操作 Body 的情况的消耗
fasthttp的实现与标准库差距较大,所以API的设计完全不同, 因此也不兼容标准库net/http。使用时既需要理解HTTP的处理过程,又需要注意和标准库的差别
fasthttp Demo
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"github.com/buaazp/fasthttprouter"
"github.com/valyala/fasthttp"
)
// index 页
func Index(ctx *fasthttp.RequestCtx) {
fmt.Fprint(ctx, "Welcome")
}
// 简单路由页
func Hello(ctx *fasthttp.RequestCtx) {
fmt.Fprintf(ctx, "hello")
}
// 获取GET请求json数据
// 使用 ctx.QueryArgs() 方法
// Peek 取某个键对应的值
func TestGet(ctx *fasthttp.RequestCtx) {
values := ctx.QueryArgs()
fmt.Fprint(ctx, string(values.Peek("abc"))) // 不加string返回的byte数组
}
// 获取post的请求json数据
// 这里就有点坑是,查了很多网页说可以用 ctx.PostArgs() 取post的参数,返现不行,返回空
// 后来用 ctx.FormValue() 取表单数据就好了,难道是版本升级的问题?
// ctx.PostBody() 在上传文件的时候比较有用
func TestPost(ctx *fasthttp.RequestCtx) {
//postValues := ctx.PostArgs()
//fmt.Fprint(ctx, string(postValues))
// 获取表单数据
fmt.Fprint(ctx, string(ctx.FormValue("abc")))
// 这两行可以获取PostBody数据,在上传数据文件的时候有用
postBody := ctx.PostBody()
fmt.Fprint(ctx, string(postBody))
}
func main() {
// 创建路由
router := fasthttprouter.New()
// 不同的路由执行不同的处理函数
router.GET("/", Index)
router.GET("/hello", Hello)
router.GET("/get", TestGet)
// post方法
router.POST("/post", TestPost)
// 启动web服务器,监听 0.0.0.0:8080
log.Fatal(fasthttp.ListenAndServe(":8080", router.Handler))
}
net/http 与 fasthttp API对比
在fasthttp中使用一个对象来维护请求的上下文:RequestCtx, 它综合了http.Request和http.ResponseWriter的操作,可以更方便的读取和返回数据
r.Body -> ctx.PostBody()
r.URL.Path -> ctx.Path()
r.URL -> ctx.URI()
r.Method -> ctx.Method()
r.Header -> ctx.Request.Header
r.Header.Get() -> ctx.Request.Header.Peek()
r.Host -> ctx.Host()
r.Form -> ctx.QueryArgs() + ctx.PostArgs()
r.PostForm -> ctx.PostArgs()
r.FormValue() -> ctx.FormValue()
r.FormFile() -> ctx.FormFile()
r.MultipartForm -> ctx.MultipartForm()
r.RemoteAddr -> ctx.RemoteAddr()
r.RequestURI -> ctx.RequestURI()
r.TLS -> ctx.IsTLS()
r.Cookie() -> ctx.Request.Header.Cookie()
r.Referer() -> ctx.Referer()
r.UserAgent() -> ctx.UserAgent()
w.Header() -> ctx.Response.Header
w.Header().Set() -> ctx.Response.Header.Set()
w.Header().Set("Content-Type") -> ctx.SetContentType()
w.Header().Set("Set-Cookie") -> ctx.Response.Header.SetCookie()
w.Write() -> ctx.Write(), ctx.SetBody(), ctx.SetBodyStream(), ctx.SetBodyStreamWriter()
w.WriteHeader() -> ctx.SetStatusCode()
w.(http.Hijacker).Hijack() -> ctx.Hijack()
http.Error() -> ctx.Error()
http.FileServer() -> fasthttp.FSHandler(), fasthttp.FS
http.ServeFile() -> fasthttp.ServeFile()
http.Redirect() -> ctx.Redirect()
http.NotFound() -> ctx.NotFound()
http.StripPrefix() -> fasthttp.PathRewriteFunc
net/http vs fasthttp 工作原理对比
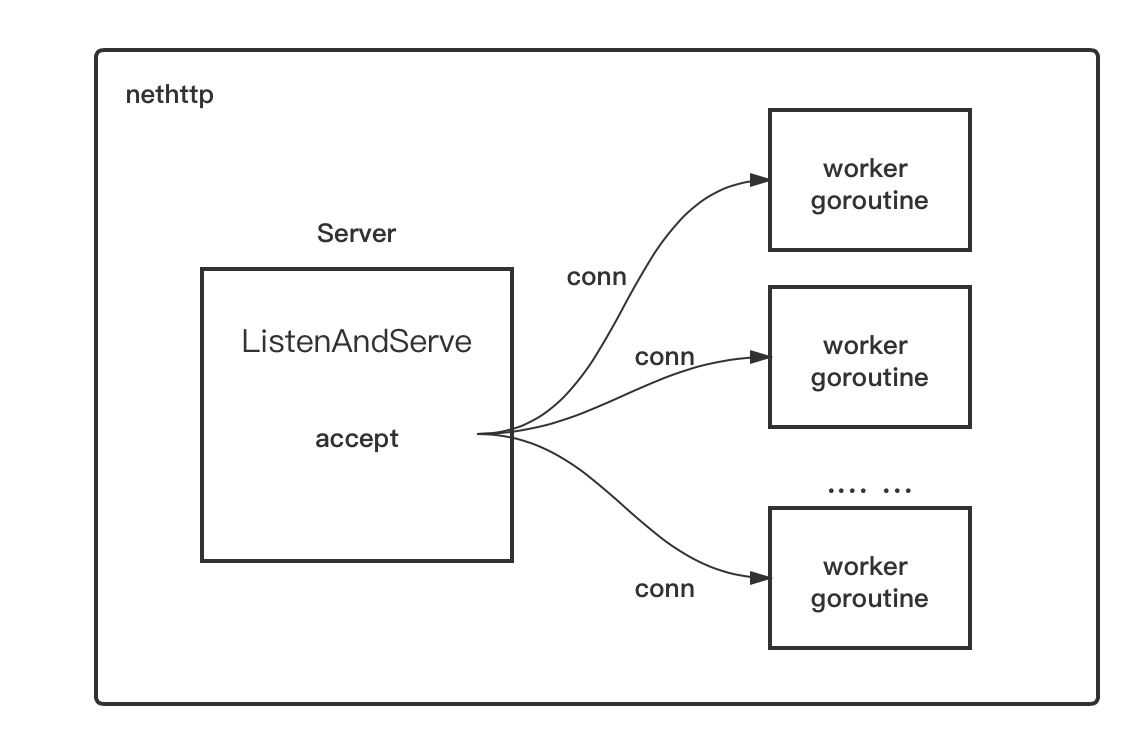
net/http包作为server端的原理很简单,那就是accept到一个连接(conn)之后,将这个conn甩给一个worker goroutine去处理,后者一直存在,直到该conn的生命周期结束:即连接关闭。
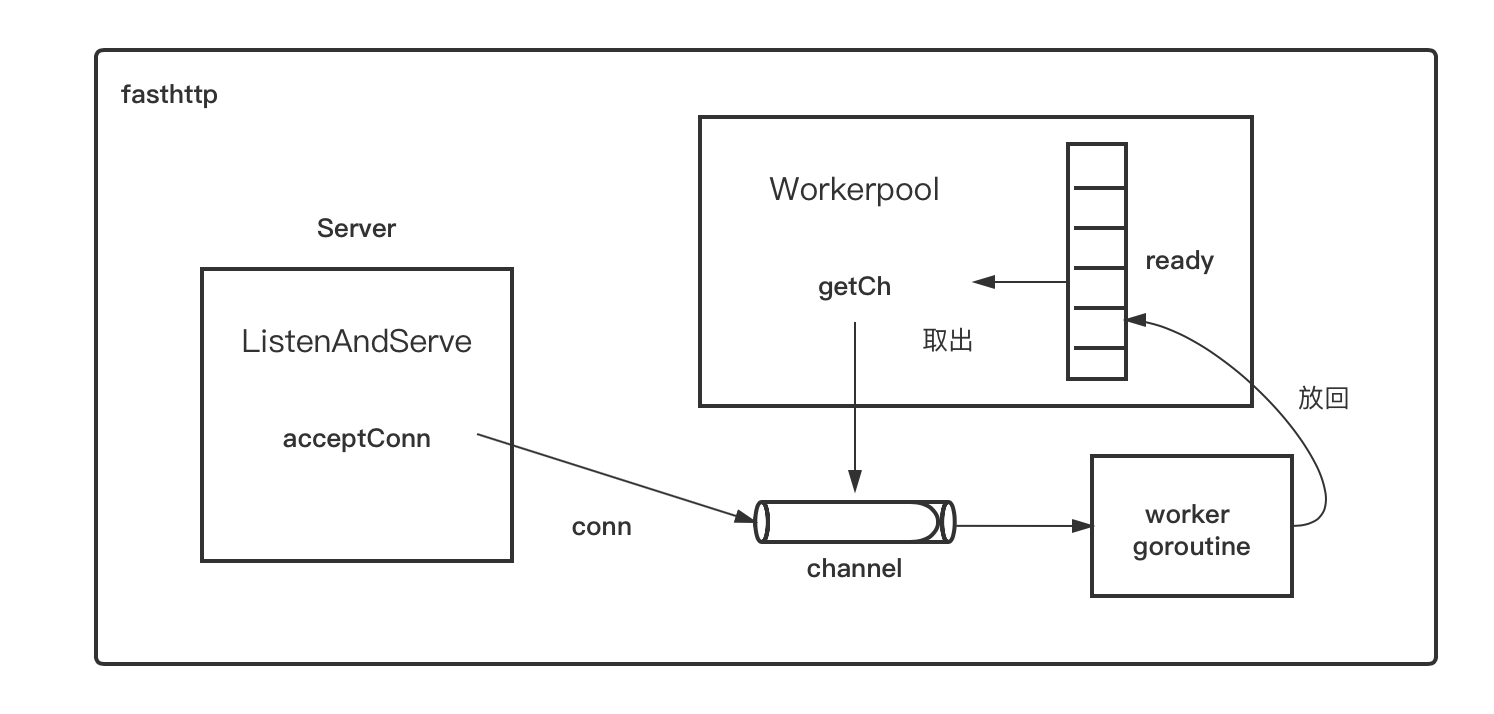
fasthttp设计了一套机制,目的是尽量复用goroutine,而不是每次都创建新的goroutine。fasthttp的Server accept一个conn之后,会尝试从workerpool中的ready切片中取出一个channel,该channel与某个worker goroutine一一对应。一旦取出channel,就会将accept到的conn写到该channel里,而channel另一端的worker goroutine就会处理该conn上的数据读写。当处理完该conn后,该worker goroutine不会退出,而是会将自己对应的那个channel重新放回workerpool中的ready切片中,等待这下一次被取出。
fasthttp 遇到的坑
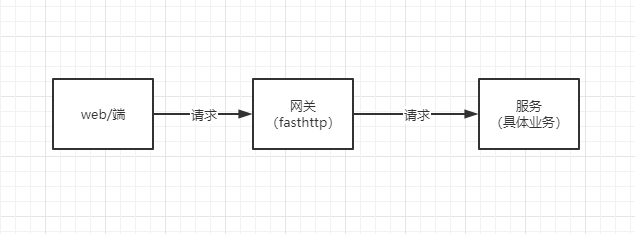 项目背景,各端通过使用fasthttp库做的网关项目请求业务接口
在线上环境中,每次请求高峰导致内存上升, 请求高峰过后内存没有回收(内存泄漏),占用内存不断增加,最后触发报警
项目背景,各端通过使用fasthttp库做的网关项目请求业务接口
在线上环境中,每次请求高峰导致内存上升, 请求高峰过后内存没有回收(内存泄漏),占用内存不断增加,最后触发报警
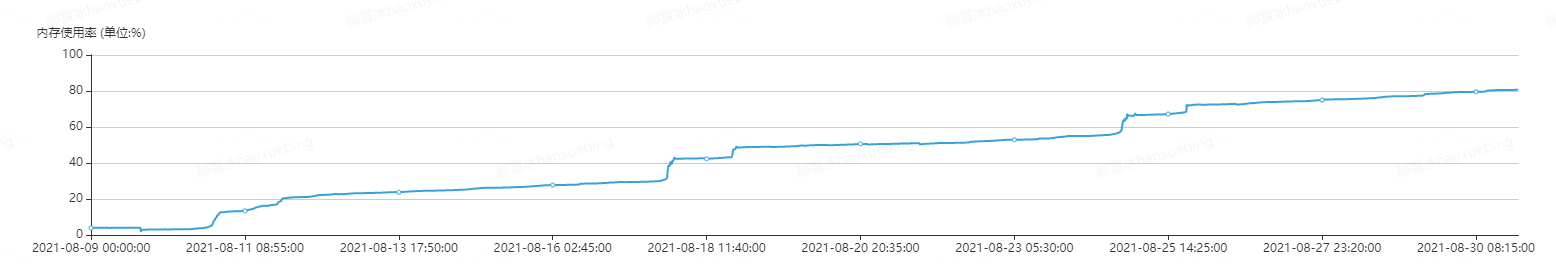
这个问题在本地压测时没有复现,压测过程中内存会上去,压测结束后内存降下来,一切正常。
原因:线上有很多异常请求,导致请求超时,然后使用fasthttp也没有设置ReadTimeout, 连接一直占用,内存得不到释放
fasthttp Demo 优化
func main() {
// 创建路由
router := fasthttprouter.New()
// 不同的路由执行不同的处理函数
router.GET("/", Index)
router.GET("/hello", Hello)
// 启动web服务器,监听 0.0.0.0:8080
server := &fasthttp.Server{
Handler: router.Handler,
ReadTimeout: 30 * time.Second,
WriteTimeout: 30 * time.Second,
Concurrency: 256 * 1024,
}
log.Fatal(server.ListenAndServe(":8080"))
}
fasthttp.Server 还有其他很多参数,Concurrency可以用来限制workerpool中并发处理的goroutine的个数,keep-alive 保持活性连接,ReadBufferSize、WriteBufferSize 读写buffer大小等等
fasthttp给出的建议
// If requests take too long and the connection pool gets filled up please
// 如果请求时间过长且连接池已满,请
// try setting a ReadTimeout.
// 尝试设置读取超时。 如果没设请求超时,也没设置Concurrency,就会导致内存泄露
参考文献
fasthttp官网
使用fasthttp搭建go的web服务器
高性能web之fasthttp
Go标准库http与fasthttp服务端性能比较
fasthttp:高性能背后的惨痛代价
一次 golang fasthttp 踩坑经验